IoT testing includes functional and integration testing relevant to the specifics of distributed architectures, performance testing to check how the app handles large volumes of streaming data, security testing at the application, gateway, and IoT device levels.
Sample lineup of an IoT testing team: a test lead and test automation lead, manual and test automation engineers, a cyber security expert.
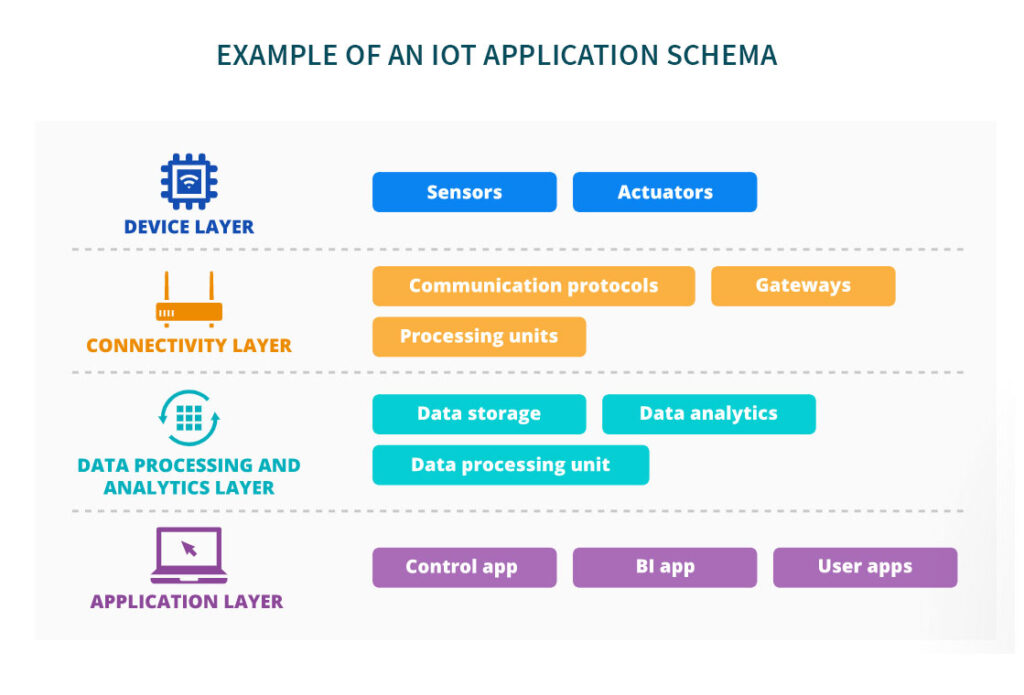
The actual IoT testing setup plan will vary depending on the IoT solution’s requirements, the chosen development model, the current SDLC stage of your IoT project.
However, our testing experts have outlined some common stages to go through.
A QA manager should be assigned as early as requirements specification development to ensure IoT functional requirements are designed in a testable way. Typically, the requirements are drawn up in a form of user stories.
The QA manager should decide how often a future QA team and the IoT development team need to collaborate to ensure relevant test cases’ prioritization, efficient defects’ management and regression testing.
Then, the QA manager should carefully consider possible IoT testing risks and design an all-around risk mitigation plan for your project. Among the risks there can be:
Lack of IoT testing talents to promptly create and execute test cases addressing potential IoT-specific quality issues
Preparation for the IoT application testing process differs based on the sourcing model you opt for: in-house testing or outsourced testing.
2.1. Preparing for in-house IoT app testing
The assigned QA manager designs an overall IoT test strategy and plan, including effort estimation. As an IoT system’s architecture is prone to changes, the QA manager needs to regularly revise and update the test artifacts accordingly.
Then, the manager assembles an IoT testing team or teams.
Testing types that our experts consider relevant for any IoT application test plan
Test engineers validate the functionality of:
Test engineers validate:
Quality data transfer between the IoT app and its third-party integrations to ensure that the data changed in one system is altered accordingly in all the connected systems, and the relevant change history is available.
To ensure an IoT application’s resilience to hacker attacks, a cyber security engineer reviews the security of the system architecture, performs the vulnerability assessment and penetration testing.
To safeguard the entire IoT system’s cyber-security, you can also opt for the security testing of:
Additionally, your IoT test plan may include performance testing to:
If you realize your in-house resources are insufficient for overarching IoT app testing, you can consider its outsourcing, as it proves to be more cost-effective than hiring and training the additional test engineers on payroll.
To select a fitting vendor, you should:
To get IoT testing started, testing teams design test cases and develop test scripts. Then, to check the end-to-end entire system’s functioning, an IoT test lab is created with the help of chosen service virtualization tools and simulators.
Perform analysis and mitigation of potential IoT application testing issues, in case of an ongoing project.
Design the IoT testing process: a test strategy and plan for the entire IoT app and for specific modules; a test automation architecture with regard to the specifics of each IoT app component; a tailored testing toolkit.
Set up and maintain the IoT test lab, generate and manage IoT test data.
Develop, execute, and maintain IoT test cases and scripts.
Create a reusable automated regression test suite for your IoT system.
© 2022 | All Rights Reserved